Implementing a Model in DuMux
What is a DuMux model
What is a DuMux model
A DuMux model is an implementation of a discretized mathematical model, generally given by partial differential equations.
What is a DuMux model
Mathematical model (PDE): \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial S(u)}{\partial t} + \nabla \cdot \mathbf{F}(u) = q(u), \quad \forall (t,\mathbf{x}) \in (0,T] \times \Omega \end{aligned} \]

What is a DuMux model
Discrete model using finite volumes: \[ \begin{aligned} \small |B| \frac{S_B(\mathbf{u}^{n+1}_h) - S_B(\mathbf{u}^{n}_h)}{\Delta t} + \sum_{\sigma \in \Sigma_B} F_{B,\sigma}(\mathbf{u}^{n+1}_h) = |B| q_B(\mathbf{u}^{n+1}_h), \quad \forall t_{n+1}\leq T, \; \forall B \end{aligned} \]
- \(B:\) control volume
- \(S_B:\) storage term
- \(F_{B,\sigma}:\) flux term over sub control volume face (scvf)
- \(q_B:\) source term
Where to implement these terms in DuMux?
LocalResidual
LocalResidual
LocalResidual
Implements terms of a PDE in the functions
computeStorage(...)computeFlux(...)computeSource(...)
Example: Diffusion equation
Mathematical model (PDE):
\[ \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial c}{\partial t} - \nabla \cdot (D \nabla c) = 0 \:\: \mathrm{in}\; \Omega \times (0,T] \end{aligned} \]
with
- \(c:\) concentration
- \(D:\) constant diffusion coefficient
- \(\Omega:\) spatial domain
- \(T:\) end time
Example: Diffusion equation
Discrete model using the Box discretization:
\[ \begin{aligned} \vert B \vert \frac{c_B^{n+1}-c_B^{n}}{\Delta t} - \sum_{\sigma \in \Sigma_{B}} \vert \sigma \vert \left[ D \nabla c_h^{n+1} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}_{B,\sigma} \right] = 0, \end{aligned} \]

Example: Diffusion equation
Discrete model using the Box discretization:
\[ \begin{aligned} \vert B \vert \frac{c_B^{n+1}-c_B^{n}}{\Delta t} - \sum_{\sigma \in \Sigma_{B}} \vert \sigma \vert \left[ D \nabla c_h^{n+1} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}_{B,\sigma} \right] = 0, \end{aligned} \]
with
- \(c_B^n:\) concentration at time \(t_n\) and control volume \(B\)
- \(c^n_h:\) global discrete solution at time \(t_n\), interpolated using basis functions
- \(\mathbf{n}:\) unit outer normal vector
- \(\sigma:\) sub control volume face (scvf)
LocalResidual
The local residual of the diffusion model:
template<class TypeTag>
class DiffusionModelLocalResidual
: public DiscretizationDefaultLocalOperator<TypeTag>
{
...
}File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Inherits from the DiscretizationDefaultLocalOperator,
which is chosen depending on the discretization scheme, here Box
scheme.
Storage term
NumEqVector computeStorage(const Problem& problem,
const SubControlVolume& scv,
const VolumeVariables& volVars) const
{
NumEqVector storage;
storage[Indices::massBalanceEqIdx]
= volVars.priVar(Indices::concentrationIdx);
return storage;
}File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Flux term
\[ \begin{aligned} F_{B,\sigma} = - \vert \sigma \vert D \nabla c_h^{n+1} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}_{B,\sigma} \end{aligned} \]
with
- \(c^n_h:\) global discrete solution at time \(t_n\), interpolated using basis functions
- \(\mathbf{n}:\) unit outer normal vector
- \(\sigma:\) sub control volume face (scvf)
Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(const Problem& problem,
const Element& element,
const FVElementGeometry& fvGeometry,
const ElementVolumeVariables& elemVolVars,
const SubControlVolumeFace& scvf,
const ElementFluxVariablesCache& elemFluxVarsCache) const
{
...
} File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(...) const
{
// Compute ∇c
const auto& fluxVarCache = elemFluxVarsCache[scvf];
Dune::FieldVector<Scalar, dimWorld> gradConcentration(0.0);
for (const auto& scv : scvs(fvGeometry))
{
const auto& volVars = elemVolVars[scv];
gradConcentration.axpy(
volVars.priVar(Indices::concentrationIdx),
fluxVarCache.gradN(scv.indexInElement())
);
}
...
}File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(...) const
{
...
NumEqVector flux;
// Compute the flux
flux[Indices::massBalanceEqIdx] = -1.0*scvf.area()*vtmv(
scvf.unitOuterNormal(),
problem.diffusionCoefficient(),
gradConcentration
);
return flux;
}File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
LocalResidual
A LocalResidual implements the discretized mathematical
model.
For its implementation different model-specific properties have to be set
Model properties
Model properties
All properties are defined within the namespace
Dumux::Properties.
File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Model type tag
The property type tag is an empty struct with the respective name,
e.g. DiffusionModel. All properties related to the desired
model can be attributed using the property type tag.
namespace Dumux::Properties::TTag {
//! The diffusion model tag that we can specialize properties for
struct DiffusionModel {};
} // end namespace Dumux::Properties::TTagFile:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Defining model properties
The type of the local residual is the class
DiffusionModelLocalResidual defined from earlier
template<class TypeTag>
struct LocalResidual<TypeTag, TTag::DiffusionModel>
{ using type = DiffusionModelLocalResidual<TypeTag>; };File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Defining model properties
The model traits specify information about the model:
template<class TypeTag>
struct ModelTraits<TypeTag, TTag::DiffusionModel>
{
struct type
{
struct Indices
{
static constexpr int concentrationIdx = 0;
static constexpr int massBalanceEqIdx = 0;
};
static constexpr int numEq() { return 1; }
};
};File:
dumux/examples/diffusion/model.hh
Defining model properties
Further model specific properties can be set accordingly by using the
model property tag, i.e. TTag::DiffusionModel
Exercise: Model
Exercise: Model
Implementation of a nonlinear diffusion model for denoising of an MRI image
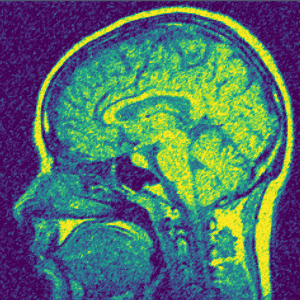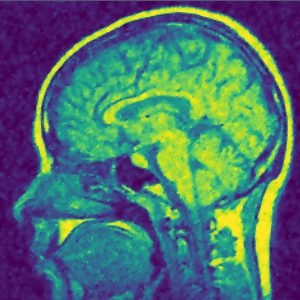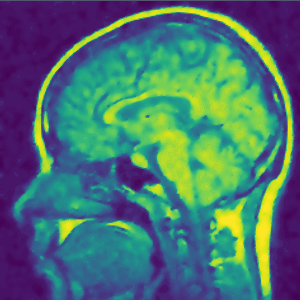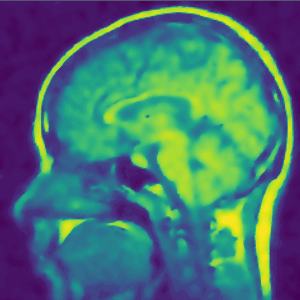
Tasks
Implement local residual
Set model properties
Use model in test case
Customize volume variables
Go to Model exercise